String strip(), lstrip(), rstrip() method
Use method strip() to remove all the leading and trailing spaces. Use method lstrip() to remove
all the leading spaces. Use the method rstrip() to remove all the trailing spaces.
#Declare a string str=" HELLO WORLD! " #Print print(str.strip()) Output: HELLO WORLD! #Declare a string str=" Hello World! " #Print print(str.lstrip()) Output: Hello World! #Declare a string str="Hello World! " #Print print(str.rstrip()) Output: Hello World!
String split() method
Use the method split() to split a string into a list of strings. A delimiter is an optional parameter. If no parameter is passed, it splits the string at each occurrence of whitespace.
#Declare a string
str="A B C D E F G H"
#use split() method
strList=str.split()
#Print
print(strList)
Output:
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H']
#Declare a string
str="20,30,50,60"
#use split() method
strList=str.split(",")
#Print
print(strList)
Output:
['20', '30', '50', '60']
Length of a string
In Python, len() method is used to find the length of the string.
#Declare a string
str='Hello World!'
strLen=len(str)
#Print
print(f"{Length of a given string is: {strLen}")
Output:
Length of a given string is: 12
Looping through strings:
Strings in Python can be looped through the for-loop, just like we loop through a list or any collection.
#For Loop
for x in "California":
print(x)
Output:
C
a
l
i
f
o
r
n
i
a
#For Loop using index
strCity="Sacramento"
for x in len(strCity):
print(strCity[x])
Output:
S
a
c
r
a
m
e
n
t
o
#For Loop using index to print the string in reverse
strCity="Houston"
for x in range(-1,-len(strCity)-1,-1):
print(strCity[x])
Output:
n
o
t
s
u
o
H
#Count no of times 'o' occurs in a string
strCity="Houston"
count=0
for x in range(len(strCity)):
if(strCity[x]=='o'):
count=count + 1
print(f"The number of occurrences of 'o' is: {count}")
Output:
The number of occurrences of 'o' is: 2
String upper() method
Use the method upper() to convert string to the uppercase.
#Declare a string str="I am going to Chicago" #Convert to uppercase strUpper=str.upper() #Print print(strUpper) Output: I AM GOING TO CHICAGO
String find() and index() method
Use the method find() to return the index of the first occurrence of a portion of the string or a character passed in the find() method. It returns -1 if the substring is not found. index() works the same way as find(). If a substring is not found, index() raises a ValueError.
#Declare a string
str="I am going to Chicago"
#Index of "Chicago" in the string
strFind=str.find("Chicago");
#Print
print(strFind)
Output:
14
#Index of "City" in the string
strFind=str.find("City");
#Print
print(strFind)
Output:
-1
#Index of "City" using index()
strFind=str.index("City");
#Print
print(strFind)
Output:
ValueError: substring not found
String lower() method
Use the method lower() to convert string to the lowercase.
#Declare a string str="I am going to Chicago" #Convert to lowercase strLower=str.lower() #Print print(strLower) Output: i am going to chicago
Check if all characters in string are uppercase:
Use the method isupper() to check if all the characters in a string are uppercase. If all the characters are uppercase, it returns True otherwise it returns False.
#Declare a string str="I am buying a HOUSE." #Check if all characters are uppercase checkUpper=str.isupper() #Print print(checkUpper) Output: False #Declare a string str="I AM BUYING A HOUSE." #Check if all characters are uppercase checkUpper=str.isupper() #Print print(checkUpper) Output: True
Check if all characters in string are lowercase:
Use the method islower() to check if all the characters in a string are lowercase. If all the characters are lowercase, it returns True otherwise it returns False.
#Declare a string str="I am going to Chicago." #Check if all characters are lowercase checkLower=str.islower() #Print print(checkLower) Output: False #Declare a string str="i am going to chicago." #Check if all characters are lowercase checkLower=str.islower() #Print print(checkLower) Output: True
Count number of times an item occurs in a string:
Use the method count() to get the number of times a character, sequence of characters or a word appears in a string.
#Declare a string
str="I am going to Houston to see my Dad."
#No of times 'am' appears in the string
intCount=str.count("am")
#Print
print(intCount)
Output:
2
String Slicing
Use the method replace() to replace a portion of a string with a new value. An optional integer argument can be passed to define the number of occurrences to be replaced. Negative slicing is also supported in Python. In negative indexing, -1 refers to the last element. -2 refers to the 2nd last element.
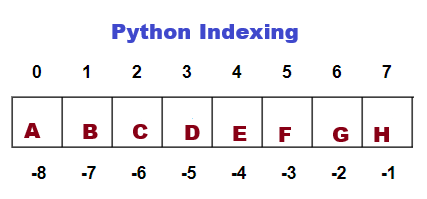
#Declare a string str="ABCDEFGH" #Extract 4th character in th string strChar=str[3] #Print print(strChar) Output: D #Extract 6th character in the string strChar=str[5] #Print print(strChar) Output: F #Extract 4 Characters starting from 'C' strChar=str[2:6] #Print print(strChar) Output: CDEF #Return the entire string strChar=str[:] #Print print(strChar) Output: ABCDEFGH #Return the entire string strChar=str[::] #Print print(strChar) Output: ABCDEFGH #Return last character strChar=str[-1] #Print print(strChar) Output: H #Return 2nd last character strChar=str[-2] #Print print(strChar) Output: G #reverse a string strChar=str[::-1] #Print print(strChar) Output: HGFEDCBA Extract 'B' to 'G' strChar=str[-7:-1] #Print print(strChar) Output: BCDEFG
String replace()
String slicing refers to extracting part of a string. Let us see some examples of String Slicing in Python. The
#Declare a string
str="I like watching cricket games, but I don't play cricket."
#Replace 'cricket' with 'baseball'
strReplace=str.replace('cricket','baseball')
#Print
print(strReplace)
Output:
I like watching baseball games, but I don't play baseball.