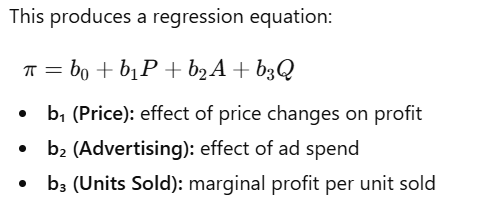|
PythonPlaza -
Python & AI
|
Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms
Decision Trees
The decision tree is called that because it creates models for classification or prediction in the shape of a tree. It splits the data into smaller parts and connects each part with a decision. This makes a tree with decision points and final answers. A decision point can have two or more paths and leads to the final answers. A final answer shows the result of the classification or decision. It uses the if-then-else rule to make predictions. As you go deeper into the tree, the rules get more complicated, which makes the model more accurate. A decision tree has:
Root Node: The process starts at the top of the tree with the entire dataset.
Internal Nodes (Decision Nodes): At each internal node, the algorithm tests a specific attribute or feature to split the data into smaller, more homogeneous subsets.
Leaf Nodes (Terminal Nodes): The process ends at the leaf nodes, which represent the final decision, class label, or predicted continuous value.

Let's see an example
 USE CASE 1: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn, predict the product price. The Production cost, Advertising spend, and Demand level are the independent variables.
USE CASE 1: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn, predict the product price. The Production cost, Advertising spend, and Demand level are the independent variables.
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_error
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
data = pd.read_excel("product_data.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Production_Cost', 'Advertising_Spend', 'Demand_Level']]
y = data['Product_Price']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# -----------------------------------
# 5. Model parameters
# -----------------------------------
print("\nIntercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients:")
for feature, coef in zip(X.columns, model.coef_):
print(f" {feature}: {coef}")
# -----------------------------------
# 6. Evaluate the model
# -----------------------------------
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("\nModel Evaluation:")
print("R² Score:", r2)
print("Mean Absolute Error:", mae)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)
# -----------------------------------
# 7. Predict price for a new product
# -----------------------------------
new_product = pd.DataFrame({
'Production_Cost': [68],
'Advertising_Spend': [13],
'Demand_Level': [37]
})
predicted_price = model.predict(new_product)
print("\nPredicted Product Price:", predicted_price[0])
USE CASE 2: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn to predict the Student Grade. The 'Hours_Studied, 'Attendance_%', 'Previous_Score' are the independent variables.

import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
# https://pythonPlaza.com/linear_school_grade_data.html
data = pd.read_excel("student_data.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Hours_Studied', 'Attendance_%', 'Previous_Score']]
y = data['Final_Grade']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# -----------------------------
# Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# -----------------------------
# Evaluation
print("Predicted grades:", y_pred)
print("Actual grades: ", y_test)
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
Example: Predict a new student’s grade
# New student: [hours_studied, attendance %, previous_score]
new_student = np.array([[6, 85, 78]])
predicted_grade = model.predict(new_student)
print("Predicted final grade:", predicted_grade[0])
USE CASE 3: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn to predict the Profit Optimization. The Price (P), Advertising (A), Units Sold (Q) are the independent variables, and Profit is the dependent variable.
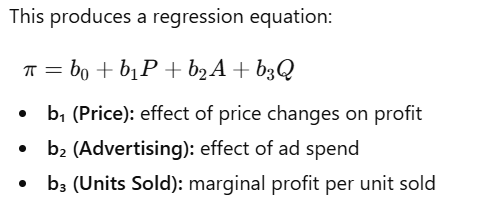
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
Get the Profit Optimization data in Excel
data = pd.read_excel("profit_optimization.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target Price (P)
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Price', 'Advertising', 'Units_Sold']]
y = data['Profit']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Predict profit
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Predicted profit:", y_pred)
print("Actual profit: ", y_test)
#Evaluate the model
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
#Profit equation (key for optimization)
print("Intercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients [Price, Advertising, Units Sold]:", model.coef_)
#Predict profit for a new business strategy
# Example: Price = 15, Advertising = 165, Units Sold = 460
new_strategy = np.array([[15, 165, 460]])
predicted_profit = model.predict(new_strategy)
print("Predicted profit:", predicted_profit[0])
USE CASE 4: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn to predict the Patient Response. The Dosage (mg), Age (yrs), Weight (lbs) are the independent variables, and Patient Response is the dependent variable.

import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
Get the Patient Response Data in Excel
data = pd.read_excel("patient_dosage_response.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target Price (P)
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Dosage', 'Age', 'Weight']]
y = data['Patient_Response']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Predict profit
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Predicted responses:", y_pred)
print("Actual responses: ", y_test)
#Evaluate the model
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
#Profit equation (key for optimization)
print("Intercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients [Dosage, Age, Weight]:", model.coef_)
Predict response for a new patient
# New patient: Dosage=72mg, Age=36yrs, Weight=172lbs
new_patient = np.array([[72, 36, 172]])
predicted_response = model.predict(new_patient)
print("Predicted patient response:", predicted_response[0])